Now, We discuss Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory. Success stands as one of the most significant goals in the lives of all human beings. This concept of success doesn’t merely refer to economic prosperity or wealth; it encompasses achieving complete personal satisfaction and living a meaningful, purposeful life. However, since the background, experiences, and specific needs of every successful person are unique, the question of what steps must be taken first to achieve success remains a complex puzzle for many people.
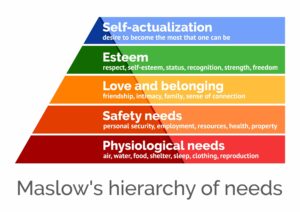
By systematically analyze these intricate human desires, Abraham Maslow who is a prominent psychologist of the 20th century presented his “Hierarchy of Needs” theory in 1943 through his paper, “A Theory of Human Motivation.” This theory clearly illustrates human needs using a five-tiered pyramid model and firmly told that a person can only enthusiastically pursue higher-level goals once the foundational, basic needs are fulfilled.
Detailed Study of Maslow’s Five Levels of Needs
According to Maslow’s theory, an individual must stably progress through the following four lower levels to reach the highest pinnacle of Self-Actualization.

(1) Physiological Needs (The Foundation)
This level represents all things essential for a human being’s physical survival. They are the fundamental building blocks of the entire hierarchy. These necessities include breathing, Water, Food, Shelter, warmth, and rest, as well as the need for Sex (reproduction).
In Maslow’s view, if a person is constantly struggling for daily sustenance and shelter, their mind cannot focus on other matters, such as career advancement or personal growth. Therefore, fulfilling this level is the key foundation for constructing all other subsequent needs.
(2) Safety Needs
Once the basic biological needs are met, humans begin to crave a stable and secure environment. This need for safety encompasses not only physical security from danger but also psychological security.
For example, job stability (financial security), health insurance, protection against loss of property, and the social stability provided by adhering to rules and laws are requirements of this stage. Without security, anxieties and worries hinder psychological progress.
(3) Love and Belonging Needs
After an individual achieves physical and environmental security, they naturally seek connection and affiliation with their social environment.
Therefore, warm relationships with family, strong friendships, acceptance as a member of a community or group, and romantic partnership are all vital components of this level. It is only when this need is met that a person’s emotional strength becomes solid.
(4) Esteem Needs
Individuals who reach this stage desire to transcend mere acceptance by others and seek self-respect (Self-Esteem). This need is associated with dignity, achievement, a sense of competence, the ability to work independently, status, and respectful recognition from others in society.
A high sense of Confidence is the results of fulfilling this level. Once this need is satisfied, a person is considered psychologically ready to fully utilize their potential.
(5) Self-Actualization (The Peak)
This is the highest level of Maslow’s pyramid and represents humanity’s ultimate psychological goal. Reaching this stage means fully expressing one’s talents, visions, and capabilities to authentically create the life one wishes to live.
Individuals at this stage are aware of their true purpose and tend to focus continually on their success. Maslow frequently cited figures like Albert Einstein as examples of people who achieved this Self-Actualization level.
The Role of Visualization in Achieving Success
To successfully maintain the highest level of Self-Actualization, an individual must continuously focus on their goals. The technique of Visualization serves as a crucial aid in making this focus effective and powerful.
What Visualization means:
- It is the practice of clearly and distinctly creating and repeatedly seeing images in the mind of the future state they wish to reach, the successful image they want to possess, and the person they want to become, even though it has not yet physically manifested.
- This mental practice of seeing the goal provides both psychological strength and practical direction for overcoming real-life obstacles.
- It is important to organize and save the data and images of our life goals like essential “Data Folders/Files” by reviewing and practicing them regularly to boost motivation.
In conclusion, by understanding Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, an individual can identify where they currently stand in life and then can complete life and ultimate success.









